Ocean-based carbon dioxide removal ocean CDR via nutrient fertilization refers to the addition of micronutrients eg iron Fe andor macronutrients eg phosphorus P nitrogen N silica Si to the surface ocean with the deliberate intent to 1 increase photosynthesis by marine phytoplankton and thus enhance uptake of carbon dioxide CO2 from surface waters and to. The male gamete or sperm and the female gamete egg or ovum are specialized sex cells which fuse together to begin the formation of a zygote during a process called sexual reproduction.
A well researched phenomenon.
. The aspects that require consideration in fertilizer application are listed below. How to test if Iron Fertilization works. Iron Fertilization Overview.
It is one of a number of business ideas that have grown out of the global demand for carbon trading. In past experiments we. The sOFeX ex-periment employed three research ships helicopter scouts and 76 scientists to moni-tor the results of adding one to two tons of iron to the ocean.
Primarily contractions of the uterus and fallopian tubes assist in sperm movement but later on they move by their own motility. The typical method involves drizzling acidified iron sulfate into the ocean as a thin slurry to reduce the amount that immediately sinks out of the sunlit surface waters where photosynthesis happens. But economists conclude that the growing urgency to solve our emissions problem will reward anyone who can make iron fertilization work.
Students will analyze data from iron fertilization studies to answer the scientific question of whether or not iron fertilization increases biological productivity and carbon sequestration. However they are declining at a very rapid pace now. Consideration of irons importance to phytoplankton growth and photosynthesis dates to the 1930s when English biologist Joseph Hart speculated that the oceans great desolate zones a.
During this process semen comprising thousands of sperms are inseminated into the female vagina during coitus. Since the 1990s scientists have proposed the idea of fertilizing the water with iron released from ships to accelerate the growth of phytoplankton. Iron fertilization companies would earn profits by measuring how much carbon they sequester and then selling the equivalent to companies or people that either wish to or are required to offset their emissions.
From the vagina the sperms travel up the uterus but only a few thousand find their way into the openings of the fallopian tubes. Appraise the value and impact of iron on chlorophyll levels. Any plan to sell sequestered carbon requires a reliable accounting and this promises to be difficult in the ocean.
This experiment is based on the fact that in about one-third of the surface ocean the growth of phytoplankton is limited by the lack of iron. Comparison of eight iron experiments shows that maximum Chl a the maximum DIC removal and the overall DICFe efficiency all scale inversely with depth of the wind mixed layer WML defining the light environment. Describe ocean iron fertilization the biological pump and upwelling.
The thinking goes like this. That iron availability limits phytoplankton in HNLC waters. Only a few sperms will succeed in reaching the opening of the fallopian tube.
It involves the addition of a large quantity of iron and other micronutrients to the ocean to improve the productivity of microscopic marine plants to the extent that they increase the intake of atmospheric carbon by the ocean eliminate it from. Availability of nutrients in manures and fertilizers. The phytoplankton response has varied in different in situ iron experiments due to differences in light availability patch mixing and dilution and grazing by zooplankton.
Iron fertilization is one of the earliest approaches that were adopted to reduce the greenhouse effect. The concentration of SF 6 would indicate the amount of dilution the original injection of Fe had undergone and regression of parameters such as p CO 2 and Chl against SF 6 at several times postinjection would enable the degree of fertilization to be assessed. -Increase in the amount of phytoplankton because of Iron -BUT little to no carbon export observed.
Iron addition is simple in principle but once a ship is loaded up and heading for open waters even small experiments be-come a tangle of logistics. Nevertheless these in situ experiments have confirmed the first part of the iron hypothesis. The sperms move towards the uterus and reach the opening of the fallopian tube.
The typical method involves drizzling. In this process we intentionally seed the ocean with iron that causes phytoplankton or algae to grow. In humans the process of fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube.
Relate roles of phytoplankton productivity and upwelling. Nutrient requirements of crops at different stages of crop growth. Adding the iron requires a 12-hour zigzagging cruise across a theoretical square of water whose boundaries shift constantly in the ocean currents.
Moreover lateral patch dilution sea surface irradiance temperature and grazing play additional roles. Distinguish among differences in chlorophyll temperature nitrate and iron levels during and after upwelling events. Phytoplankton release an immense amount of oxygen into the atmosphere.
Ocean iron fertilization is one of the various methods of eradicating atmospheric carbon dioxide. Sperms swim in the fluid medium at the rate of 15 to 3 mm per minute to reach the site. The Southern Ocean experiments were most.
Methods of application placement of fertilizers. Iron is a vital micronutrient that phytoplankton need to grow but its generally scarce in the ocean. Students engaged in this activity examine the scientific and ethical dimensions of iron fertilization as a geoengineering strategy to mitigate global warming.
The process is called Iron fertilization and is designed to take carbon out of the atmosphere to help you mitigate your contribution to global warming. Rather than feed the growth of extra plankton triggering algal blooms the iron fertilization may instead stimulate the gluttonous diatoms to take up even more iron to build larger shells. This modeling study suggests not only mixed layer depth but also the initial biomass of diatoms and its principle grazers are crucial factors 20in the response of the phytoplankton community to the iron enrichments and should be considered in designing future iron-enrichment experiments.
The ab-sence of clear regulations for either conducting experiments at sea or trading the results in carbon offset markets complicates the picture. Fertilization is the process by which male and female gametes are fused together initiating the development of a new organism. -Enrich area by adding Iron along with inert and sensitive tracer -Follow what happens through time by ship-board measurements and satellite observations What were the results of the Iron Fertilization test.
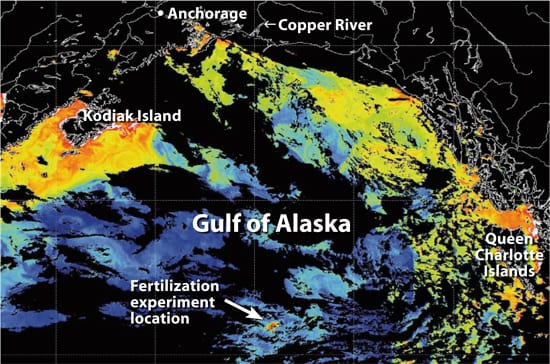
Fertilizing The Ocean With Iron Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution

Seeding The Seas With Iron East Bay Times

Dumping Iron And Trading Carbon Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
0 Comments